February 21, 2017
Virtualbox has various mode of networking between host-guest and guest-guest, few basic modes are as follows.
- NAT :
- This is default configuration for virtualbox, it allow virtual machine to talk to internet.
- VM acts like a computer that connects to the Internet through a router. The “router”, in this case, is the VirtualBox networking engine, which maps traffic from and to the virtual machine transparently.
- Since vm is behind nat( virtualbox router), hence isn’t directly accessible to host machine. To communicate with guest machine(running on virtualbox), we can use port forwarding.
- In port forwarding a host-port is mapped with guest-port and data coming to mapped port can be moved from guest to host and vice-versa.
- NAT Network : A internal network where vm’s can talk to each other but outside machines cannot access the vm’s and all traffic from vm’s connected to that network is sent via Nat interface.
- In Nat network we create a nat network from virtualbox settings(not vm settings).
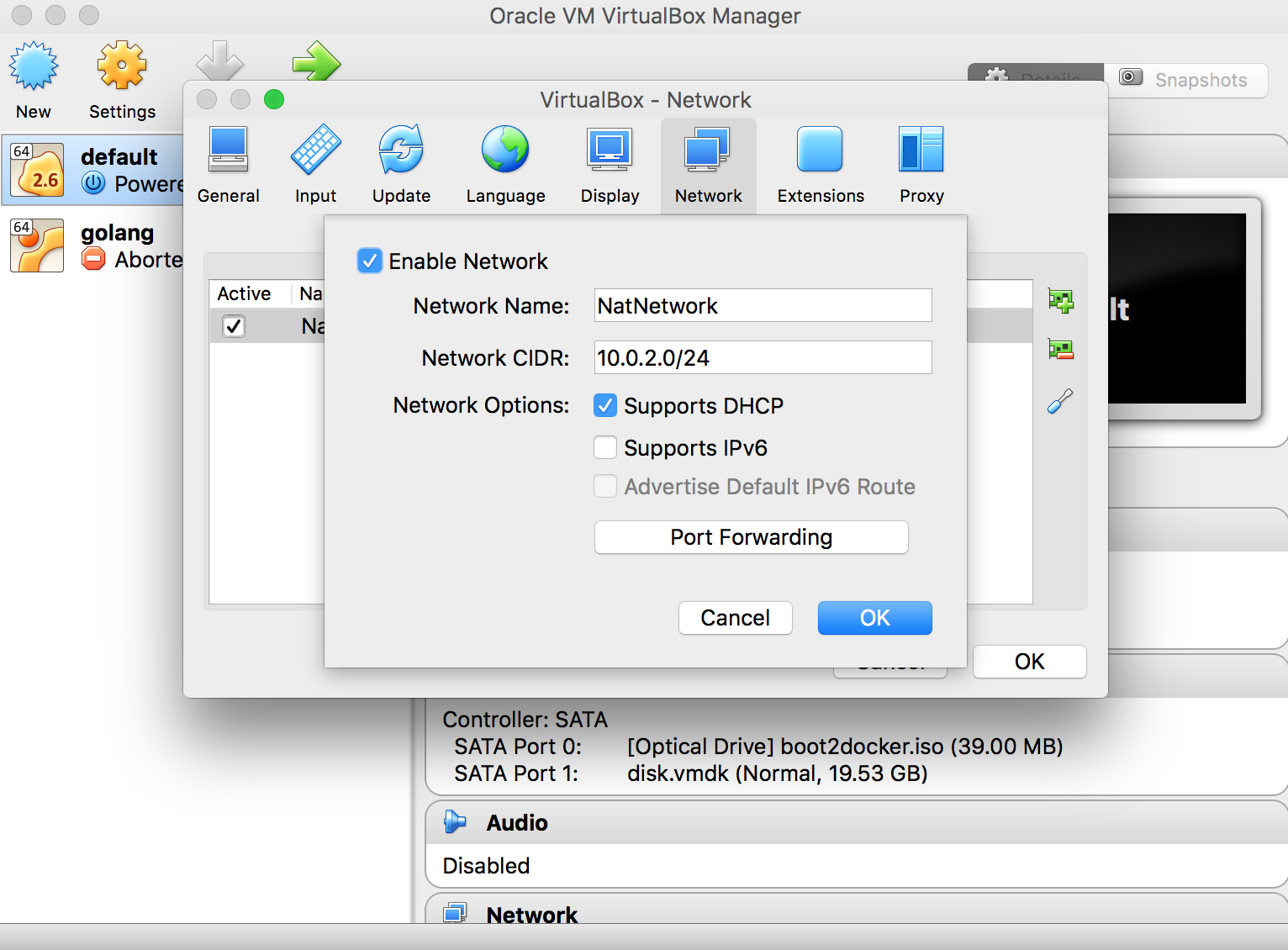 .
. - In network configuration of vm we select that specific nat network from dropdown and we are ready for communicating with machines in network.
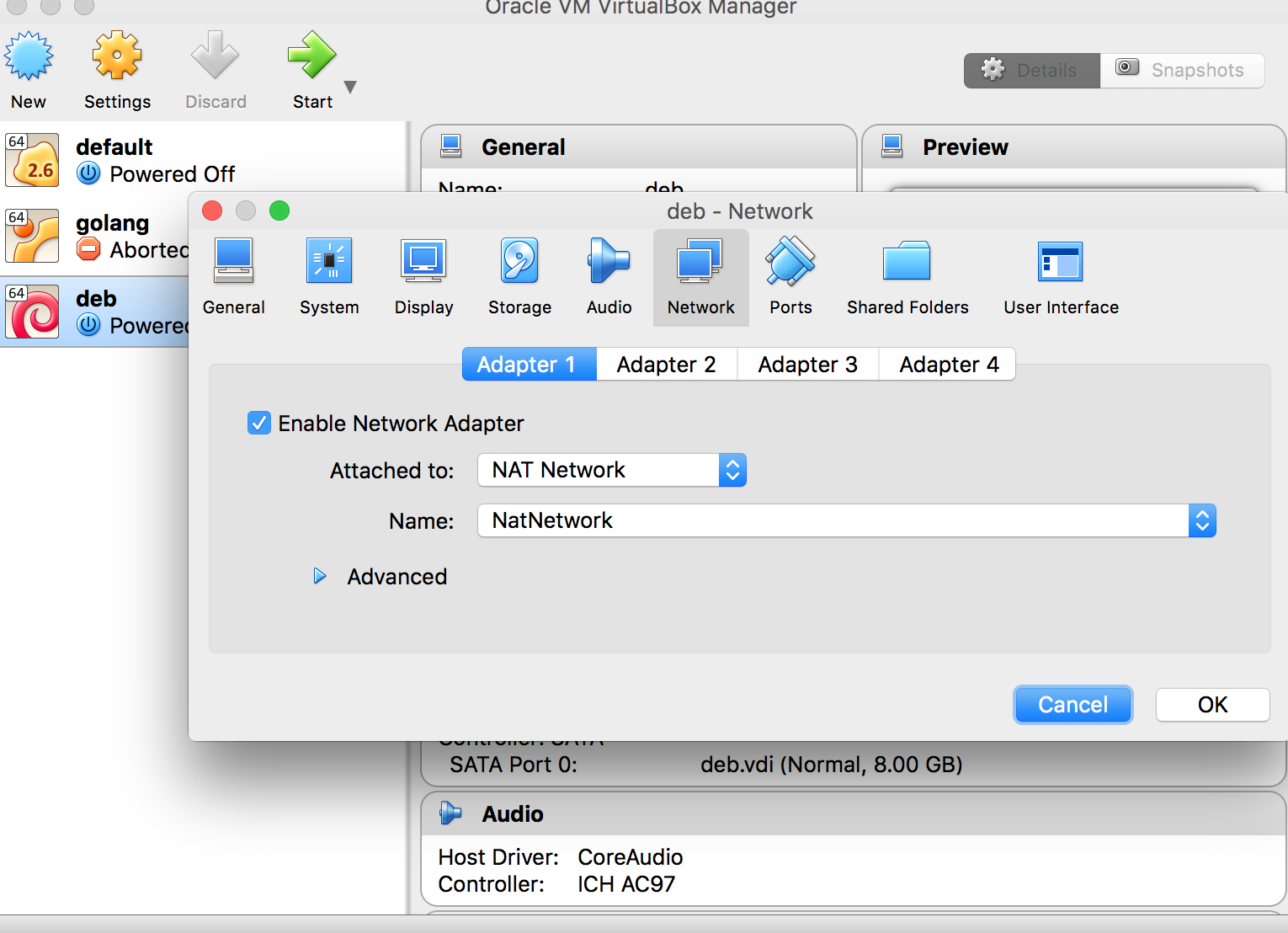
- It is similar to home network behind router,
- (copy pasted –> )A NAT service is attached to an internal network. Virtual machines which are to make use of it should be attached to that internal network. The name of internal network is chosen when the NAT service is created and the internal network will be created if it does not already exist.
- In Nat network we create a nat network from virtualbox settings(not vm settings).
- Bridged networking :
- With bridged networking, virtualbox uses a device driver on host system that filters data from physical network adapter
- It intercepts data from physical network and injects data into into it, effectively creating software network interface
- When a guest is using such a new software interface, it looks to the host system as though the guest were physically connected to the interface using a network cable: the host can send data to the guest through that interface and receive data from it.
- We can set routing or bridging between the guest and the rest of your network.
- Internal networking :
- In Internal networking the machine can talk to each other only.
- Network name is the identifer that connects two nodes in the internal network.
- The traffic between the machine cannot be sniffed as no physical interface is used
- No internet access
- No direct access(ssh to machine or any connection) to vms
- Host-only networking :
- Host only networking is hybrid between the bridged and internal networking modes.
- In bridge networking the communication virtual machines(vm’s) can talk to each other and the host as if they were connected through a physical Ethernet switch.
- In internal networking however, a physical networking interface need not be present, and the virtual machines cannot talk to the world outside the host since they are not connected to a physical networking interface.
- A new software interface is created on the host and it is used for communication instead of existing physical interfaces.
- The traffic is moved using the new interface created, hence your traffic can be seen through the interfaces.
- Host only networking is hybrid between the bridged and internal networking modes.
Reference : https://www.virtualbox.org/manual/ch06.html